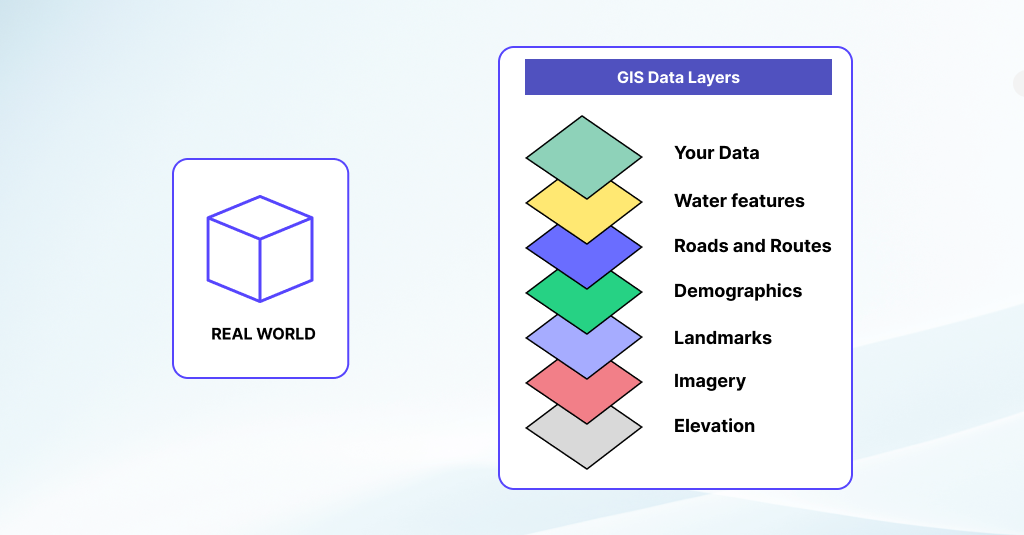
What is a Geographic Information System (GIS)?
A Geographic Information System (GIS) is a powerful computer-based tool that captures, stores, manages, analyzes, and presents spatial or geographic data. At its core, GIS combines geographic data (such as maps, satellite imagery, and GPS coordinates) with attribute data (such as population demographics, land use, and environmental characteristics) to create detailed and interactive maps, visualizations, and analyses.
Geographic Information System Benefits and Functionalities
GIS allows users to explore, interpret, and understand spatial relationships, patterns, and trends across various scales and dimensions. Through spatial analysis, a Geographic Information System enables users to perform complex geospatial calculations, such as proximity analysis, spatial clustering, and overlay analysis, to derive valuable insights and inform decision-making processes. This includes identifying spatial patterns, detecting trends, modeling spatial relationships, and assessing spatial distributions of phenomena.
A Geographic Information System has diverse applications across numerous industries and disciplines. In urban planning and development, GIS is used to assess land suitability, plan transportation networks, allocate zoning districts, and optimize urban growth and infrastructure. In natural resource management, GIS supports monitoring and analysis of land use, vegetation cover, water resources, and wildlife habitats to inform conservation efforts and sustainable resource management practices.
Furthermore, a Geographic Information System plays a vital role in emergency management and response, providing spatial data analysis, situational awareness, and decision support tools during disasters, emergencies, and crisis situations. It helps identify vulnerable areas, plan evacuation routes, coordinate response efforts, and allocate resources effectively to mitigate risks and protect communities.
Moreover, GIS is increasingly employed in public health applications for disease surveillance, epidemiological analysis, and health resource planning. It aids in identifying disease outbreaks, analyzing spatial patterns of health outcomes, assessing healthcare access, and supporting public health interventions and policy decisions.
Relevance in the Travel Industry
A Geographic Information System (GIS) enables businesses to analyze and visualize spatial data for better decision-making. GIS allows travel companies to map out tourist attractions, transportation networks, and accommodation options, providing a comprehensive view of a destination. This technology enhances route planning, helps identify emerging travel trends, and supports targeted marketing efforts by understanding customer preferences based on geographic patterns. By leveraging GIS, travel agencies can offer personalized experiences, optimize logistics, and improve overall service delivery, making it an essential component in the modern travel ecosystem.
Conclusion
GIS serves as an indispensable tool for spatial data analysis, visualization, and decision-making across a wide range of domains, including urban planning, natural resource management, emergency response, public health, and business intelligence. Its ability to integrate, analyze, and interpret spatial data makes GIS a valuable asset for understanding the complex relationships between geography, environment, society, and economy.